Network Simulator
Phase 61/67 (67%)
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Concept
Developing agentic AI systems and network automation tools requires rapid iteration. Spinning up containers for every test cycle takes minutes; simulation takes seconds. This simulator enables fast prototyping of network automation agents, DevOps pipelines, and AI-driven network operations — validate configurations and agent logic in simulation before committing to heavyweight container deployments.
Quick Facts
| Status | Phase 61/67 (67%) |
| Language | Rust |
| Started | 2026 |
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Why the Network Simulator?
- Validate before deploying — Catch routing loops, black holes, and misconfigurations in simulation
- Deterministic execution — Same topology, same results, every time
- Protocol fidelity — Real OSPF/IS-IS SPF calculations, MPLS label operations, BFD failure detection
- Advanced features — MPLS/LDP, SR-MPLS, RSVP-TE, GRE tunnels, L3VPN with VRFs, BFD, BMP telemetry
- Daemon mode — Run simulations as background services, attach interactive consoles with tab completion
- Scriptable — JSON output for CI/CD integration and automated testing
- Fast — Simulate 100+ device topologies in seconds
Quick Start — Three-Router OSPF Example
Create ospf-triangle.yaml:
name: ospf-triangle
description: Three OSPF routers in a triangle with hosts
devices:
- name: r1
type: router
router_id: 1.1.1.1
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.12.1/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: eth1
ip: 10.0.13.1/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: eth2
ip: 10.0.1.1/24
- name: r2
type: router
router_id: 2.2.2.2
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.12.2/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: eth1
ip: 10.0.23.2/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: r3
type: router
router_id: 3.3.3.3
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.13.3/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: eth1
ip: 10.0.23.3/24
ospf: { area: 0, cost: 10 }
- name: eth2
ip: 10.0.3.1/24
- name: h1
type: host
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.1.10/24
gateway: 10.0.1.1
- name: h3
type: host
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.3.10/24
gateway: 10.0.3.1
links:
- endpoints: [r1:eth0, r2:eth0]
- endpoints: [r1:eth1, r3:eth0]
- endpoints: [r2:eth1, r3:eth1]
- endpoints: [r1:eth2, h1:eth0]
- endpoints: [r3:eth2, h3:eth0]
script:
- at: converged
device: r1
command: show ip route
- at: converged + 100
device: h1
command: ping 10.0.3.10
Run the simulation:
$ netsim run ospf-triangle.yaml
[t=0ms] Network initialized: 5 devices, 5 links
[t=0ms] OSPF: r1, r2, r3 sending Hello on all interfaces
[t=10ms] OSPF: Neighbors established (r1<->r2, r1<->r3, r2<->r3)
[t=15ms] OSPF: LSA flooding in progress
[t=20ms] OSPF: SPF calculation complete on all routers
[t=20ms] Network converged
[t=20ms] r1> show ip route
10.0.1.0/24 directly connected (eth2)
10.0.3.0/24 via 10.0.13.3 [OSPF/110] metric=11
10.0.12.0/24 directly connected (eth0)
10.0.13.0/24 directly connected (eth1)
10.0.23.0/24 via 10.0.12.2 [OSPF/110] metric=20
[t=120ms] h1> ping 10.0.3.10
PING 10.0.3.10: 64 bytes from 10.0.3.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=2.1ms
Round-trip path: h1 -> r1 -> r3 -> h3 -> r3 -> r1 -> h1
Simulation complete: 120ms simulated, 0.034s real time (3529x speedup)
Discussion:
- Topology loaded — 3 routers, 2 hosts, 5 links
- OSPF converged — Routers exchanged LSAs, computed SPF
- Routes installed — FIBs populated with best paths
- Commands executed —
show ip route,pingran at scripted times - Results output — ASCII tables showing routing tables and ping responses
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Demo
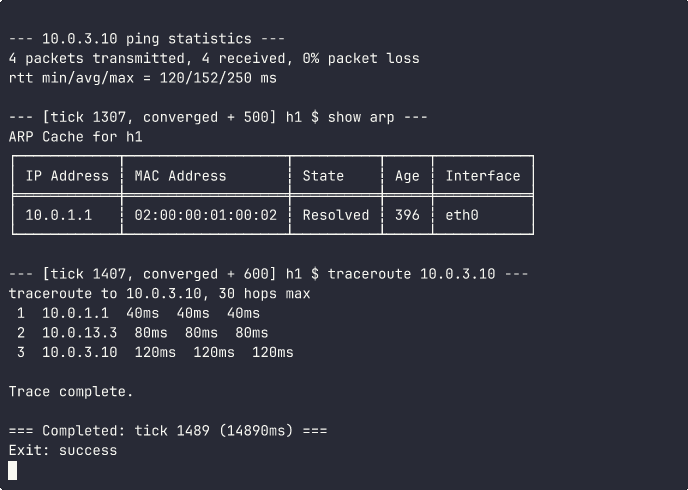 OSPF triangle: three routers form adjacencies, compute SPF, then a host pings across the network. ARP resolution, traceroute hop-by-hop path discovery, and convergence timing all visible.
OSPF triangle: three routers form adjacencies, compute SPF, then a host pings across the network. ARP resolution, traceroute hop-by-hop path discovery, and convergence timing all visible.
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Daemon Mode — Real-Time Network Interaction
Run simulations as background daemons and interact with them in real-time — like docker exec for network simulations.
Starting a Daemon
# Network Simulator
netsim daemon start my-network topology.yaml
# Network Simulator
netsim daemon start my-network topology.yaml --tick-interval 50ms
The daemon runs continuously in the background, ticking the simulation at the specified interval. State files are stored in ~/.netsim/<name>/ — PID file, Unix domain socket for gRPC IPC, and structured log.
Execute One-Shot Commands
Run a single command against a device in a running daemon, get the result, and exit. Ideal for scripting and CI/CD:
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec my-network r1 "show ip route"
Destination Next Hop Metric Interface
10.0.1.0/24 — 0 eth2 (connected)
10.0.3.0/24 10.0.13.3 11 eth1 (OSPF)
10.0.12.0/24 — 0 eth0 (connected)
10.0.13.0/24 — 0 eth1 (connected)
10.0.23.0/24 10.0.12.2 20 eth0 (OSPF)
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec my-network h1 "ping 10.0.3.10"
Ping 10.0.3.10: 5/5 packets received, 0% loss
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec my-network r1 "show ip route --json"
[{"destination":"10.0.1.0/24","next_hop":"—","metric":0,"interface":"eth2","source":"connected"}, ...]
Attach an Interactive Console
netsim attach my-network r1
Opens a full interactive REPL session on the device. You’re effectively “logged in” to the simulated router with command history, tab completion, and abbreviated commands:
r1> sh ip ro
Destination Next Hop Metric Interface
10.0.1.0/24 — 0 eth2 (connected)
10.0.12.0/24 — 0 eth0 (connected)
10.0.13.0/24 — 0 eth1 (connected)
10.0.3.0/24 10.0.13.3 11 eth1 (OSPF)
10.0.23.0/24 10.0.12.2 20 eth0 (OSPF)
r1> show interfaces
Interface IP Address MAC Address Admin Status
eth0 10.0.12.1/24 02:00:00:00:01:00 up up
eth1 10.0.13.1/24 02:00:00:00:01:01 up up
eth2 10.0.1.1/24 02:00:00:00:01:02 up up
r1> show ospf neighbors
Neighbor ID Interface State Priority Dead Time
2.2.2.2 eth0 Full 1 38s
3.3.3.3 eth1 Full 1 36s
r1> show arp
IP Address MAC Address State Age Interface
10.0.12.2 02:00:00:00:02:00 Resolved 396 eth0
10.0.13.3 02:00:00:00:03:00 Resolved 396 eth1
Live interface management — shut down a link and watch the protocol reconverge in real time:
r1> interface shutdown eth0
Interface eth0 admin-down
[OSPF adjacency r1<->r2 torn down]
r1> sh ip ro
Destination Next Hop Metric Interface
10.0.1.0/24 — 0 eth2 (connected)
10.0.13.0/24 — 0 eth1 (connected)
10.0.3.0/24 10.0.13.3 11 eth1 (OSPF)
10.0.23.0/24 10.0.13.3 21 eth1 (OSPF)
← traffic to r2 now routes via r3 (metric increased from 20 to 21)
r1> interface no shutdown eth0
Interface eth0 admin-up
[OSPF adjacency r1<->r2 re-establishing...]
r1> sh ip ro
← routes restored to original paths after reconvergence
JSON output on any show command for structured data:
r1> show ospf neighbors --json
[{"neighbor_id":"2.2.2.2","interface":"eth0","state":"Full","priority":1},
{"neighbor_id":"3.3.3.3","interface":"eth1","state":"Full","priority":1}]
Console Features:
- Abbreviated commands — Prefix matching (
sh ip ro→show ip route,int shut→interface shutdown) - Tab completion — Full hierarchical completion for commands, subcommands, and arguments
- Interface management —
interface shutdown/no shutdowntriggers protocol teardown and reconvergence - JSON output — Append
--jsonto any show command for structured output - Command history — Arrow keys navigate previous commands
- MPLS operations —
mpls lfib add/del,mpls ftn add/delfor label manipulation - VPN commands —
bgp vpn-originate,show bgp vpn,show vrffor L3VPN troubleshooting - GRE tunnels —
gre tunnel setfor overlay configuration - MPLS OAM —
mpls ping,mpls traceroutefor label-switched path verification
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
TUI Daemon Selector
Running netsim daemon with no subcommand launches an interactive TUI (built with ratatui) that lets you browse running daemons, select devices, and attach — all without memorizing names.
Level 1 — Daemon selector lists all running simulations:
┌─ Running Daemons ─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ > ospf-triangle (PID 48291, 2h 15m) │
│ examples/ospf-triangle.yaml │
│ │
│ sp-core (PID 48305, 45m 12s) │
│ topologies/transitnet-sp-core.yaml │
│ │
│ dc-fabric (PID 49102, 3m 8s) │
│ topologies/spine-leaf-evpn.yaml │
│ │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Up/Down: Navigate Enter: Select l: Logs q: Quit
Press Enter to select a daemon, then Level 2 — Device selector shows all devices:
┌─ ospf-triangle: Devices ──────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ > r1 (router) │
│ r2 (router) │
│ r3 (router) │
│ h1 (host) │
│ h3 (host) │
│ │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Up/Down: Navigate Enter: Select l: Logs q: Back
Press Enter on a device to open an interactive console session. Press l at any point to open the log viewer showing real-time daemon events (protocol state changes, adjacency transitions, convergence events).
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Daemon Management
# Network Simulator
$ netsim daemon list
NAME PID UPTIME TOPOLOGY
ospf-triangle 48291 2h 15m examples/ospf-triangle.yaml
sp-core 48305 45m 12s topologies/transitnet-sp-core.yaml
# Network Simulator
$ netsim daemon status my-network
Daemon: my-network
PID: 48291
Uptime: 2h 15m 30s
Tick interval: 100ms
Topology: examples/ospf-triangle.yaml
Devices: r1 (router), r2 (router), r3 (router), h1 (host), h3 (host)
# Network Simulator
$ netsim daemon stop my-network
# Network Simulator
$ netsim daemon list --clean
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
CI/CD Integration Example
Start a daemon, run automated validation, collect results, tear down:
#!/bin/bash
# Network Simulator
# Network Simulator
netsim daemon start ci-test topology.yaml --tick-interval 10ms
# Network Simulator
sleep 2
# Network Simulator
ROUTES=$(netsim exec ci-test r1 "show ip route --json")
OSPF=$(netsim exec ci-test r1 "show ospf neighbors --json")
PING=$(netsim exec ci-test h1 "ping 10.0.3.10")
# Network Simulator
echo "$ROUTES" | jq -e '.[] | select(.destination == "10.0.3.0/24")' || exit 1
echo "$OSPF" | jq -e 'length == 2' || exit 1
echo "$PING" | grep -q "0% loss" || exit 1
# Network Simulator
netsim daemon stop ci-test
echo "All validations passed"
Failover Testing with Daemon Mode
Test link failure and reconvergence interactively:
# Network Simulator
$ netsim daemon start failover-test sp-core.yaml
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec failover-test r1 "show ospf neighbors"
Neighbor ID Interface State Priority Dead Time
2.2.2.2 eth0 Full 1 38s
3.3.3.3 eth1 Full 1 36s
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec failover-test r1 "interface shutdown eth0"
Interface eth0 admin-down
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec failover-test r1 "show ip route"
10.0.23.0/24 10.0.13.3 21 eth1 (OSPF)
# Network Simulator
$ netsim exec failover-test r1 "interface no shutdown eth0"
$ sleep 1
$ netsim exec failover-test r1 "show ospf neighbors"
Neighbor ID Interface State Priority Dead Time
2.2.2.2 eth0 Full 1 38s ← re-established
3.3.3.3 eth1 Full 1 36s
Why Use Daemon Mode?
- Agentic AI development: Test automation agents against live network state without container overhead — agents can execute commands, parse responses, and iterate in seconds rather than minutes
- Network automation prototyping: Rapidly develop and test configuration management tools, DevOps scripts, and automated network operations
- Fast iteration loop: Design → Generate configs → Simulate → Iterate, all without spinning up containers until you’re ready to deploy
- CI/CD integration: Start daemon, run automated tests via
exec, collect JSON results, stop daemon - Development workflow: Keep a topology running while you experiment with agent logic or automation scripts
- Structured logging: Daemon events logged in JSON to
~/.netsim/<name>/daemon.logfor debugging and post-mortem analysis
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Protocol Support
Layer 2
| Protocol | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet | ✓ | MAC addressing, frame encapsulation |
| ARP | ✓ | Request/reply, cache management |
Layer 3
| Protocol | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 | ✓ | Forwarding, TTL decrement, fragmentation not supported |
| ICMP | ✓ | Echo (ping), Time Exceeded (traceroute), Destination Unreachable |
Routing Protocols
| Protocol | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Static | ✓ | Host default gateway |
| OSPF | ✓ | Point-to-point, Area 0, LSA Types 1 & 2, SPF via Dijkstra |
| IS-IS | ✓ | L1/L2 hierarchical routing, LSP flooding, SPF via Dijkstra |
| BGP | ✓ | iBGP/eBGP, communities, route reflectors, MP-BGP VPNv4 |
MPLS & Tunneling
| Protocol | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MPLS | ✓ | Label imposition/swap/pop/pop-continue, LFIB, multi-label stacks |
| LDP | ✓ | Label distribution, targeted sessions |
| SR-MPLS | ✓ | Segment Routing with SRGB, Node-SIDs, SR-owned LFIB precedence |
| RSVP-TE | ✓ | Explicit-path tunnels, deterministic refresh, convergence gating |
| GRE | ✓ | Generic routing encapsulation, overlay tunnels |
| VRF | ✓ | Virtual routing and forwarding, L3VPN with RD/RT |
Resilience & Telemetry
| Protocol | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| BFD | ✓ | Bidirectional forwarding detection, async mode |
| BMP | ✓ | RFC 7854 BGP Monitoring Protocol, post-decision export |
| PCAP | ✓ | Packet capture with MPLS-aware filtering, Wireshark compatible |
Available Commands
All commands support prefix abbreviation (e.g., sh ip ro) and --json output for structured data.
Show Commands (Read-Only Introspection):
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show ip route [vrf <name>] |
Routing table (global or per-VRF) |
show interfaces |
Interface status, IP, MAC, admin state |
show arp |
ARP cache entries |
show ospf neighbors |
OSPF adjacency state |
show ospf database |
OSPF LSDB contents |
show isis neighbors |
IS-IS adjacency state |
show isis database |
IS-IS LSDB contents |
show isis interfaces |
IS-IS interface status |
show isis spf |
IS-IS SPF run information |
show isis route |
IS-IS routing table |
show bgp [summary] |
BGP Loc-RIB / neighbor overview |
show bgp neighbors [<ip>] |
BGP neighbor details |
show bgp vpn |
VPNv4 routes |
show mpls [forwarding] |
MPLS FTN/LFIB tables |
show mpls vpn-labels |
VPN label allocations |
show ldp [bindings/neighbors] |
LDP session and label state |
show bfd [sessions] |
BFD session status |
show gre [tunnels] |
GRE tunnel status |
show vrf [<name> [routes]] |
VRF list, details, or per-VRF routes |
show sr |
Segment Routing state and SIDs |
show rsvp [tunnels] |
RSVP-TE tunnel status |
show traffic |
Traffic generator statistics |
Data Plane Probes:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
ping <ip> [-c N] |
ICMP echo test |
traceroute <ip> [-m TTL] |
Hop-by-hop path discovery |
mpls ping <ip> [--vrf <name>] |
MPLS OAM echo test |
mpls traceroute <ip> [--vrf <name>] |
MPLS OAM path discovery |
Operational Configuration:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
route add <dest> via <nexthop> |
Add static route |
interface shutdown <name> |
Admin-down interface (triggers protocol reconvergence) |
interface no shutdown <name> |
Admin-up interface |
mpls lfib add/del <label> ... |
Manipulate MPLS LFIB entries |
mpls ftn add/del <prefix> ... |
Manipulate MPLS FTN entries |
bgp vpn-originate <vrf> |
Trigger VPN route origination |
gre tunnel set <iface> ... |
Configure GRE tunnel parameters |
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Example: IS-IS L1/L2 Hierarchy with Real Output
Service provider topology demonstrating IS-IS hierarchical routing:
name: isis-hierarchy
description: IS-IS L1/L2 hierarchy with inter-area routing
devices:
- name: r1
type: router
isis:
net: "49.0001.0000.0000.0001.00"
level: l1
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.1.0.1/24
isis: { metric: 10 }
- name: lo
ip: 192.0.2.1/32
isis: {}
- name: r2
type: router
isis:
net: "49.0001.0000.0000.0002.00"
level: l1l2 # Area border router
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.1.0.2/24
isis: { metric: 10 }
- name: eth1
ip: 10.0.0.2/24
isis: { metric: 10 }
- name: lo
ip: 192.0.2.2/32
isis: {}
- name: r3
type: router
isis:
net: "49.0002.0000.0000.0003.00"
level: l2
interfaces:
- name: eth0
ip: 10.0.0.3/24
isis: { metric: 10 }
- name: lo
ip: 192.0.2.3/32
isis: {}
links:
- endpoints: [r1:eth0, r2:eth0]
- endpoints: [r2:eth1, r3:eth0]
script:
- at: converged
device: r2
command: show isis neighbors
- at: converged
device: r2
command: show isis database
- at: converged
device: r1
command: show ip route
Simulation Output:
$ netsim run isis-hierarchy.yaml
[t=0ms] Network initialized: 3 devices, 2 links
[t=0ms] IS-IS: r1, r2, r3 sending IIH (IS-IS Hello)
[t=3ms] IS-IS: Adjacencies forming
[t=5ms] IS-IS: r1<->r2 L1 adjacency Up
[t=5ms] IS-IS: r2<->r3 L2 adjacency Up
[t=8ms] IS-IS: LSP flooding in progress
[t=12ms] IS-IS: SPF calculation complete (L1 and L2)
[t=12ms] Network converged
[t=12ms] r2> show isis neighbors
System ID Interface State Level Holdtime
0000.0000.0001 eth0 Up L1 24s
0000.0000.0003 eth1 Up L2 24s
[t=12ms] r2> show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num Checksum Lifetime Attributes
0000.0000.0001.00-00 0x00000003 0x4a2e 864 L1
0000.0000.0002.00-00 0x00000003 0x5c1a 864 L1L2
IS-IS Level-2 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num Checksum Lifetime Attributes
0000.0000.0002.00-00 0x00000003 0x7f3c 864 L1L2
0000.0000.0003.00-00 0x00000003 0x9a2b 864 L2
[t=12ms] r1> show ip route
Codes: C - connected, i L1 - IS-IS level-1, i L2 - IS-IS level-2
C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, eth0
C 192.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, lo
i L1 192.0.2.2/32 [115/10] via 10.1.0.2, eth0
i L2 192.0.2.3/32 [115/20] via 10.1.0.2, eth0
(route leaked from L2 to L1 by ABR r2)
Simulation complete: 15ms simulated, 0.008s real time
IS-IS events: 18 hellos, 4 LSPs, 2 SPF runs
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Use Cases
- Agentic AI & Network Automation Development: Rapidly prototype and test automation agents, DevOps pipelines, and AI-driven network operations with seconds-long iteration cycles instead of minutes spinning up containers
- Configuration Generation Testing: Validate Network Modeling & Configuration Library-generated configs in simulation before deploying to Containerlab — catch errors in the generation logic early
- Network Automation Prototyping: Develop configuration management tools, automated provisioning systems, and orchestration scripts against realistic network topologies without infrastructure overhead
- Pre-deployment Validation: Catch routing loops, black holes, and misconfigurations before production
- Convergence Analysis: Measure failover time and validate backup paths
- Training: Safe environment for learning routing protocol behavior and automation development
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77
Milestones
v1.0 MVP (Shipped Jan 24, 2026) Tick-based simulation engine with deterministic execution.
- Layer 2/3 forwarding (Ethernet, ARP, IPv4), ICMP (ping, traceroute)
- OSPF routing with adjacency formation, LSA flooding, and SPF calculation
- YAML topology input, scripted command execution
v1.1 Scale & Features (Shipped Jan 31, 2026) Parallel execution, BGP, and traffic generation.
- Tokio parallel execution with adaptive thresholds
- Full BGP protocol (iBGP/eBGP, path selection, communities)
- Traffic generation (CBR, Poisson, burst patterns), latency/loss modeling
- Multi-access OSPF with DR/BDR election
v1.2 Engine Hardening (Shipped Jan 31, 2026) Convergence detection and dynamic topology changes.
- Quiescence detection with configurable stability window
- Dynamic wire/device removal with cascade cleanup
v1.3 Automation (Shipped Feb 1, 2026) Python bindings and REST API.
- Python bindings via PyO3 (
netsim-pypackage) - REST API with OpenAPI documentation, SSE real-time events
v1.4 Observability & Export (Shipped Feb 1, 2026) Packet capture and flow export.
- Pcap/pcapng export with Wireshark compatibility
- NetFlow v9 and IPFIX (RFC 7011) export with UDP streaming
v1.5 Protocol Foundation (Shipped Feb 5, 2026) Second IGP, sub-second failure detection, tunneling, and MPLS.
- IS-IS with L1/L2 hierarchical routing, DIS election, SPF
- BFD sub-second failure detection, GRE tunnel encap/decap
- MPLS/LDP dataplane label switching and signaling, OAM ping/traceroute
- BGP hardening: route reflectors (RFC 4456), graceful restart, End-of-RIB
v1.6 L3VPN & Telemetry (Shipped Feb 11, 2026) VRF isolation, L3VPN services, RSVP-TE, and BGP monitoring.
- VRF foundations with separate RIB/FIB/ARP per VRF
- L3VPN with MP-BGP VPNv4, RD/RT import/export, VPN label stacks
- RSVP-TE explicit-path tunnels with label precedence (TE > SR > LDP > static)
- BMP export (RFC 7854) for BGP monitoring
- Daemon mode with interactive console, tab completion, TUI selector
v1.7 Segment Routing (Shipped Feb 14, 2026) SR-MPLS programming and traffic analysis.
- SR-MPLS with deterministic SRGB and Node-SID model
- Multi-label stack forwarding
- Routing matrix export and flow-based simulation engine
v1.8 Data Center Fabric & EVPN (In Progress) EVPN control plane and VXLAN dataplane for data center fabrics.
- EVPN Type 2/3/5 routes for MAC/IP advertisement
- VXLAN encapsulation/decapsulation
- Multi-tenancy with bridge domains and VRF routing
- Requirements definition phase
Roadmap:
- v1.8 Data Center Fabric & EVPN — VXLAN overlay with BGP EVPN (Type 2/3/5 routes), ESI multi-homing and LACP simulation, multicast foundation (PIM-SM, IGMP/MLD)
- v1.9 Chaos Engineering & Performance — Scripted chaos injection with blast radius analysis, BGP hijack simulation, SoA memory layout and zero-copy parallel execution, incremental FIB updates, QoS with WRR and priority queuing
- v2.0 Intelligent Simulation — Distributed engine with remote participation via gRPC, simulation time machine with state snapshot and rewind debugging, LLM-powered troubleshooting CLI
- v2.1 Ecosystem & Digital Twin — Hybrid real-sim bridge via TUN/TAP for host connectivity, config ingestion from Cisco/Juniper to netsim YAML
Tech Stack
Rust, Tokio for async execution, petgraph for topology representation, gRPC for daemon IPC, ratatui for TUI
Roadmap
- v1.9 IPv6 Foundation (Proposed) — Phases 68-72
- v2.0 Enterprise & Campus Protocols (Proposed) — Phases 73-74
- v2.1 Advanced Transport (Proposed) — Phases 75-77